How Tekla Structures automatically attaches rebar set bars to concrete parts
When you create or modify a rebar set, Tekla Structures automatically attaches each bar in the rebar set to a concrete part. This concrete part is the parent part of the rebar set bar.
Depending on the cast unit type, bottom level, and volume of the concrete parts, and the bar length, location, and orientation, and the number of bars in the rebar set, Tekla Structures searches for and chooses the parent part for each of the bars as follows:
-
Each bar that is at least partly inside only one concrete part is attached to that part.
-
Each bar that is inside both precast and cast-in-place concrete parts is attached to a precast part.

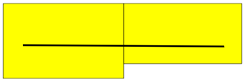
(1) = precast part, (2) = cast-in-place part
In this and the following images, the parent part is shown in green.
Then, for each bar that is inside two or more concrete parts, either precast parts or cast-in-place parts, but not both:
-
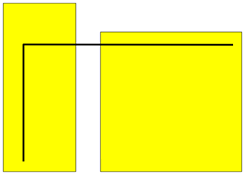
A bar is considered horizontal if its overall horizontal extent H is longer than or equal to its overall vertical extent V multiplied by the default factor of 2. Otherwise the bar is considered vertical.

(1) = horizontal bar, (2) = vertical bar
In general, a bar in a rebar set is considered horizontal if:
H ≥ XS_REBAR_VERTICAL_FACTOR * V
-
If the bar is considered horizontal, it is attached to the part that contains the longest bar length.
-
If the bar is considered vertical and if the bar is fully inside one part and partially inside other parts, it is attached to the part that contains the whole bar.
-
If the bar is considered vertical and placed partly inside several parts, it is attached to the part whose bottom face has the lowest global z coordinate.
Sometimes several parts might match one of the above criteria and could be the parent part of a rebar set bar. For example:
|
|
A horizontal bar is equally in two parts. |
|
|
Two parts contain some of a vertical bar and their bottom levels are at equal height. |
|
|
Two parts contain all of a vertical bar but are at different heights. |
In cases like these, Tekla Structures chooses the parent part for each bar from among the matching parts as follows:
-
If one of the parts is the more common parent part in the rebar set than the other parts, Tekla Structures attaches the bar to that more common parent part.
For example:
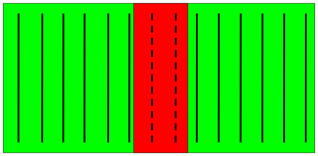
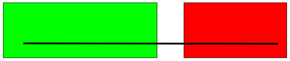
In this plan or elevation view, two parts overlap and the dashed bars are entirely in both parts.
The dashed bars are attached to the green part because it contains more bars of the rebar set than the red part.
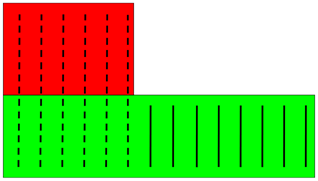
In this plan view, the dashed bars are in two parts. The bar planes are vertical and the parts are at equal height.
The dashed bars are attached to the green part because the most bars of the rebar set are attached to it.
-
If there is no more common parent part for a rebar set, Tekla Structures attaches the bar to the part that has the smallest volume.
For example:
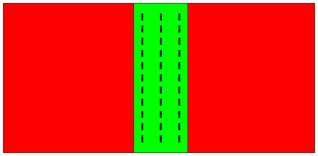
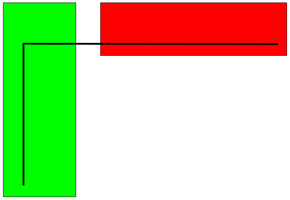
In this plan view, two parts overlap and a rebar set with the dashed bars is entirely in both parts.
The bars are attached to the green part because it has the smaller volume.
If the volumes of the parts are equal for several parts, Tekla Structures chooses the part with the smallest ID.
If you need to override the automatic attachment of rebar set bars to concrete parts, you can manually attach rebar sets and bars in them.