Verification Example - Glulam Beam Design (ASD)
Description
This verification example utilizes Tekla Tedds to check the capacity of a glulam beam that supports purlins. This example is based on Design Example E1.3 of 2015/2018 Structural Wood Design Examples by American Wood Council (AWC) (pages 16 to 20). Comparisons and contrasts are tabularized and discussed regarding the results from Tedds and the AWC Design Example. The Tedds file used in this example is provided in the Tedds “Select Calculation” window, under Verification Examples.
Problem statement
Design a simple roof supporting beam spanning 32 ft., with 5000 lb. loads (1000 lb. dead load (DL) + 4000 lb. snow load (SL)) applied by purlins at 8 ft. on center (at ¼ points plus the ends). Member has lateral supports at the ends and compression edge supports at the purlin locations. Beam supports are 6 inches long. Assume dry service conditions. Temperature is less than 100 degrees (F) but occasionally may reach 150 degrees (F). Use 24F-1.8E structural glued laminated (glulam) Southern Pine timber.
References
2015/2018 Structural Wood Design Examples by American Wood Council
2018 National Design Specification for Wood Construction
Tedds calculation
Wood member analysis & design (NDS 2018) - Compared using version 2.2.26
Example information
Glulam beam information:
Size: 5x22 (the Design Example's first iteration is 5x30.25. The second and final iteration (5x22) is used to verify the results)
Stress Grade: 24F-E1 SP/SP is used. The Design Example states the grade is 24F-1.8E, but to use the correct volume factor (x=20) for Southern Pine, the design values from Table 5A Expanded are used.
Bearing length = 6”
Unbraced length - major axis = 32’-0”
Unbraced length - minor axis = 8’-0”
Effective length factor - minor axis = 1.54L = 148”
Reference and Adjusted Design Values:
Fbx+ = 2,400 psi
Fbx- = 1,450 psi
Fc⟂,compressive face = 650 psi
Fc⟂,tension face = 805 psi
Fvx = 300 psi
Ft = 1,100 psi
Fc = 1,600 psi
Ex = E’x = 1,800,000 psi
Ex,min = E’x,min = 950,000 psi
CD = 1.15
CM = 1.0
Ct = 1.0 (temperatures up to 150 ℉ only occasionally occur)
Cfu = 1.0
Cc = 1.0
Cb = 1.0
CI = 1.0
Cvr = 1.0
Notes / Assumptions
-
It is out of the scope of Tekla Tedds to camber glulam members. The final result of the Design Example cambers the glulam beam ⅜”. As seen in the summary below, the deflection determined by Tedds matches the glulam beam deflection from the Design Example, minus the camber.
-
Per NDS 2018 Table 5A note 3, Fvx may be increased to 300 psi for structural glued laminated timber of Southern Pine. The Design Example utilizes a value of 265 psi. Fvx for 24F-E1 SP/SP = 300 psi, which matches note 3 and the value that Tedds utilizes.
-
The Design Example’s compression perpendicular to grain value, Fc⟂, is 650 psi. Since Tedds uses a glulam grade 24F-E1 SP/SP, Fc⟂ is dependent on tension face or compressive face. The tension face is the governing side, so Fc⟂,tension face = 805 psi per NDS 2018 Table 5A Expanded.
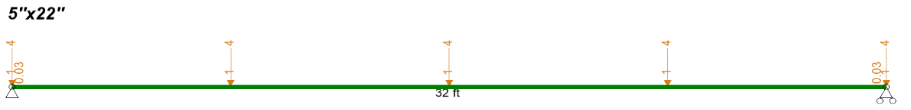
Figure 1: Glulam beam loading
| Comparison of Results between Tedds and AWC Design Example E1.3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Component | Tedds Result | AWC Design Example E1.3 | % Difference |
| Moment, M | 83.7 kip-ft | 1,006,080 in-lbf = 83.8 kip-ft | 0.1%a |
| Slenderness Ratio, RB | 11.406 | 11.406 | 0.0% |
| Reference bending design value, Fbx+* | 2,760 psi | 2,760 psi | 0.0% |
| Beam Stability Factor, CL | 0.977 | 0.978 | 0.1% |
| Volume Factor, CV | 0.95 | 0.951 | 0.1% |
| Adjusted bending stress, Fb’ | 2,625 psi | 2,625 psi | 0.0% |
| Bending stress, fb | 2,489 psi | 2,496 psid | 0.3%a |
| Shear, V | 7,956 lbs | 7,918 lbs | 0.5%a |
| Adjusted shear stress, Fv’ | 345 psi | 305 psi | 13.1%c |
| Shear stress, fv | 108 psi | 108 psi | 0.0% |
| Bearing Reaction, Rx | 12,956 lbs | 12,988 lbs | 0.2%a, b |
| Adjusted compression perp. to grain, tension face, Fc⟂, tension | 805 psie | 650 psi | 23.8%e |
| Compression perp. to grain stress, tension face, fc⟂, tension | 432 psi | 433 psi | 0.2%a, b |
| Total deflection, Δtotal | 1.843 in. | 1.843 in.f | 0.0% |
Comparison Notes:
aThe slight differences can be attributed to small differences in self-weight used. The Design Example uses a self-weight value of 30 pcf while Tedds utilizes a self-weight value of 37.3 pcf.
bThe Design Example includes the 3” past the support based on the 6” bearing length. Tedds does not include this additional beam length.
cPer NDS 2018 Table 5A note 3, Fv may be increased to 300 psi for structural glued laminated timber of Southern Pine. The Design Example utilizes a value of 265 psi. Fv for 24F-E1 SP/SP = 300 psi, which matches note 3 and the value that Tedds utilizes.
dThe Design Example does not directly calculate bending stress, fb. Instead, the example determines the required section modulus. However, by dividing the moment from the Design Example by the utilized section modulus of a 5x22 glulam beam, the bending stress can be determined.
eThe Design Example’s compression perpendicular to grain value, Fc⟂, is 650 psi. Since Tedds uses a glulam grade 24F-E1 SP/SP, Fc⟂ is dependent on the face; tension or compression. The tension face is the governing side, so Fc⟂,tension face = 805 psi per NDS 2018 Table 5A Expanded.
fThe Design Example cambers the glulam beam ⅜”. Cambering wood members in Tekla Tedds is currently out of scope. If the camber is neglected in the Design Example, then the total deflection resultant matches the total deflection from Tekla Tedds.
Conclusion:
Upon reviewing the results above, the strength capacity determination of a glulam beam using Tekla Tedds is consistent with the result of AWC Design Example E1.3. Differences between Tedds and the example can be attributed to rounding and other slight differences due to the scope of the program and engineering judgment. Users should feel confident that results determined in the Tedds Wood Member Design module are in agreement with NDS.